 |
P37 |
March
1999
|
To be published in:
Astronomy & Astrophysics
|
About the origin of extinction in the gravitational lens system
MG J0414+0534+
M.-C. Angonin-Willaime1,
C. Vanderriest2,3,
F. Courbin4,3,5,
I. Burud4,
P. Magain4,* and
F. Rigaut6
1 DEMIRM, Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, France
2 Visiting Astronomer, Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope.
3 UMR 8631, CNRS-DAEC, Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, 92195 Meudon Cedex, France
4 Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique - Université de Liège, Avenue de Cointe 5, 4000 Liège, Belgium
5 Universidad Catolica de Chile, Departement of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Casilla 22, Santiago 22, Chile
6 European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, D-85748 Garching bei München, Germany
* Maître de Recherches FNRS, Belgium
+ Based on observations collected with the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope at Mauna Kea (Hawaii, USA), the Nordic Optical Telescope (Canary, Spain) and archive data from the Hubble Space Telescope (NASA/ESA)
Photometric measurements of the highly reddened gravitational mirage
MG J0414+0534 have been carried out either by PSF subtraction or by
applying accurate deconvolution algorithms to optical (R, I) and
near-infrared (K) images obtained at CFHT and NOT under
sub-arcsecond seeing conditions. It is confirmed that the close pair
of images A1-A2 suffers a larger extinction than B and C. While the
colours of image A2 obtained from ground-based data seem inconsistent
with a simple reddening law, higher resolution images available from
HST archives reveal an additional extended component (arc) which
introduces significant errors in the photometric decomposition. When
the arc component is properly taken into account, the colours of the 4
nucleus images do agree with a classical reddening law, with A2 being
by far the most obscured component. Such a differential extinction
(maximum difference
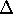 E(R-I)
E(R-I)
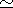 0.6) is
likely due to the
lensing galaxy. This does not mean that all the extinction
occurs into the lens. Indeed, the fact that the arc is much less red
than the images of the nucleus suggests that an important part of the
reddening is intrinsic to the source. Finally, no significant
variability is observed within this data set, i.e. between 1994 and
1997, while a discrepancy from earlier data is noticed for (A1 + A2).
0.6) is
likely due to the
lensing galaxy. This does not mean that all the extinction
occurs into the lens. Indeed, the fact that the arc is much less red
than the images of the nucleus suggests that an important part of the
reddening is intrinsic to the source. Finally, no significant
variability is observed within this data set, i.e. between 1994 and
1997, while a discrepancy from earlier data is noticed for (A1 + A2).
gravitational lensing - quasars:
individual: MG J0414+0534 - Infrared: galaxies - galaxies: ISM.
A complete HTML version is available on the
"Image
Processing of Gravitational Lenses" Page
| Article: |
mg0414.ps.gz |
(770355 bytes): |
HTTP |
admin.ago@uliege.be


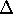 E(R-I)
E(R-I)
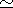 0.6) is
likely due to the
lensing galaxy. This does not mean that all the extinction
occurs into the lens. Indeed, the fact that the arc is much less red
than the images of the nucleus suggests that an important part of the
reddening is intrinsic to the source. Finally, no significant
variability is observed within this data set, i.e. between 1994 and
1997, while a discrepancy from earlier data is noticed for (A1 + A2).
0.6) is
likely due to the
lensing galaxy. This does not mean that all the extinction
occurs into the lens. Indeed, the fact that the arc is much less red
than the images of the nucleus suggests that an important part of the
reddening is intrinsic to the source. Finally, no significant
variability is observed within this data set, i.e. between 1994 and
1997, while a discrepancy from earlier data is noticed for (A1 + A2).