 |
P75 |
August
2002
|
To be published in:
The Astronomical Journal
|
Structure and dynamics of candidate O star bubbles in N44
Y. Nazé1,*,
Y.-H. Chu2,**,
M. A. Guerrero2,**,
M. S. Oey3,
R. A. Gruendl2 and
R. Chris Smith4
1 Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique - Université de Liège, Allée du 6 Août, 17, Bât. B5c, B-4000 Liège, Belgium
2 Astronomy Department, University of Illinois, 1002 W. Green Street, Urbana, IL 61801, USA
3 Lowell Observatory, 1400 West Mars Hill Rd., Flagstaff, AZ 86001, USA
4 Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, Casilla 603, La Serena, Chile
* Research Fellow FNRS, Belgium
** Visiting astronomer, Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
Dynamical studies of superbubbles and Wolf-Rayet ring nebulae show
discrepancies from the standard, adiabatic model for wind-blown bubbles.
We therefore study the physical properties and kinematics of three candidate
bubbles blown by single O stars, to evaluate whether these discrepancies are
also found in these simpler objects. Our sample candidates are N44F, N44J,
and N44M, in the outskirts of the HII complex N44 in
the Large Magellanic Cloud. We have obtained ground-based and HST
emission-line images and high dispersion echelle spectra for these objects.
From the H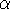 luminosities and the
[OIII]/H
luminosities and the
[OIII]/H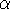 ratios of these nebulae,
we estimate the spectral types of the ionizing stars to be O7V, O9.5V and
O9.5V for N44F, N44J, and N44M, respectively. We find that the observed
expansion velocity of 12 km s-1 for N44F is consistent with the
stellar wind luminosity expected from the central ionizing star, as
predicted by the standard bubble model. The observed upper limits for the
expansion velocities of N44J and N44M are also compatible with the expected
values, within the uncertainties. We also report the discovery in N44F of
strongly-defined dust columns, similar to those seen in the Eagle Nebula.
The photoevaporation of these dense dust features may be kinematically
important and may actually govern the evolution of the shell. The inclusion
of photoevaporation processes may thus undermine the apparent agreement
between the observed bubble dynamics and the simple adiabatic models.
ratios of these nebulae,
we estimate the spectral types of the ionizing stars to be O7V, O9.5V and
O9.5V for N44F, N44J, and N44M, respectively. We find that the observed
expansion velocity of 12 km s-1 for N44F is consistent with the
stellar wind luminosity expected from the central ionizing star, as
predicted by the standard bubble model. The observed upper limits for the
expansion velocities of N44J and N44M are also compatible with the expected
values, within the uncertainties. We also report the discovery in N44F of
strongly-defined dust columns, similar to those seen in the Eagle Nebula.
The photoevaporation of these dense dust features may be kinematically
important and may actually govern the evolution of the shell. The inclusion
of photoevaporation processes may thus undermine the apparent agreement
between the observed bubble dynamics and the simple adiabatic models.
HII regions -- ISM: bubbles -- ISM: kinematics and dynamics --
ISM: individual (N44) -- Magellanic Clouds
| Article: |
n44.pdf |
(1948557 bytes): |
HTTP |
admin.ago@uliege.be


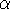 luminosities and the
[OIII]/H
luminosities and the
[OIII]/H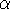 ratios of these nebulae,
we estimate the spectral types of the ionizing stars to be O7V, O9.5V and
O9.5V for N44F, N44J, and N44M, respectively. We find that the observed
expansion velocity of 12 km s-1 for N44F is consistent with the
stellar wind luminosity expected from the central ionizing star, as
predicted by the standard bubble model. The observed upper limits for the
expansion velocities of N44J and N44M are also compatible with the expected
values, within the uncertainties. We also report the discovery in N44F of
strongly-defined dust columns, similar to those seen in the Eagle Nebula.
The photoevaporation of these dense dust features may be kinematically
important and may actually govern the evolution of the shell. The inclusion
of photoevaporation processes may thus undermine the apparent agreement
between the observed bubble dynamics and the simple adiabatic models.
ratios of these nebulae,
we estimate the spectral types of the ionizing stars to be O7V, O9.5V and
O9.5V for N44F, N44J, and N44M, respectively. We find that the observed
expansion velocity of 12 km s-1 for N44F is consistent with the
stellar wind luminosity expected from the central ionizing star, as
predicted by the standard bubble model. The observed upper limits for the
expansion velocities of N44J and N44M are also compatible with the expected
values, within the uncertainties. We also report the discovery in N44F of
strongly-defined dust columns, similar to those seen in the Eagle Nebula.
The photoevaporation of these dense dust features may be kinematically
important and may actually govern the evolution of the shell. The inclusion
of photoevaporation processes may thus undermine the apparent agreement
between the observed bubble dynamics and the simple adiabatic models.