 |
P63 |
February
2001
|
To be published in:
Astronomy and Astrophysics
|
HD 152248: evidence for a colliding wind interaction+
H. Sana1,
G. Rauw1,* and
E. Gosset1,**
1 Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique - Université de Liège, Avenue de Cointe 5, 4000 Liège, Belgium
* Postdoctoral Researcher FNRS, Belgium
** Research Associate FNRS, Belgium
+ Based on observations collected at the European Southern Observatory (La Silla, Chile) and at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO)
We present the results of a four year spectroscopic campaign on the
early-type binary system HD 152248. Our analysis yields a new
classification as O7.5III(f) + O7III(f) in contradiction with previous
classifications of the components as supergiants. We derive improved
orbital elements and the corresponding masses
M1=29.6 M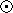 and
M2=29.9 M
and
M2=29.9 M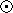 are
somewhat larger than previously reported in the literature, though they
are still significantly lower than the ones expected from evolutionary
tracks. Both components of the system are rather close to fill their
Roche lobe at periastron passage. We also investigate the equivalent
width variations of the lines of the two components and we discuss their
relation to the Struve-Sahade effect. Finally, we show that the
line profile variability of the HeII
are
somewhat larger than previously reported in the literature, though they
are still significantly lower than the ones expected from evolutionary
tracks. Both components of the system are rather close to fill their
Roche lobe at periastron passage. We also investigate the equivalent
width variations of the lines of the two components and we discuss their
relation to the Struve-Sahade effect. Finally, we show that the
line profile variability of the HeII
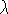 4686 and
H
4686 and
H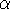 lines is consistent with a strong wind interaction between the two stars
very much as predicted by current colliding wind models.
lines is consistent with a strong wind interaction between the two stars
very much as predicted by current colliding wind models.
binaries: close -- binaries: spectroscopic -- Stars: early-type -- Stars:
fundamental parameters -- Stars individual: HD 152248 -- Stars: winds,
outflows
| Article: |
ms10575.ps.gz |
(222651 bytes): |
HTTP |
admin.ago@uliege.be


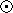 and
M2=29.9 M
and
M2=29.9 M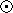 are
somewhat larger than previously reported in the literature, though they
are still significantly lower than the ones expected from evolutionary
tracks. Both components of the system are rather close to fill their
Roche lobe at periastron passage. We also investigate the equivalent
width variations of the lines of the two components and we discuss their
relation to the Struve-Sahade effect. Finally, we show that the
line profile variability of the HeII
are
somewhat larger than previously reported in the literature, though they
are still significantly lower than the ones expected from evolutionary
tracks. Both components of the system are rather close to fill their
Roche lobe at periastron passage. We also investigate the equivalent
width variations of the lines of the two components and we discuss their
relation to the Struve-Sahade effect. Finally, we show that the
line profile variability of the HeII
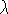 4686 and
H
4686 and
H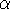 lines is consistent with a strong wind interaction between the two stars
very much as predicted by current colliding wind models.
lines is consistent with a strong wind interaction between the two stars
very much as predicted by current colliding wind models.