 |
P44 |
February
2000
|
To be published in:
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
|
ASCA spectroscopy of the hard X-ray emission from the colliding wind
interaction in  2 Velorum
G. Rauw1,2,*,
I.R. Stevens2,
J.M. Pittard2,3,
M.F. Corcoran4
2 Velorum
G. Rauw1,2,*,
I.R. Stevens2,
J.M. Pittard2,3,
M.F. Corcoran4
1 Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique - Université de Liège, Avenue de Cointe 5, 4000 Liège, Belgium
2 School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston Birmingham B15 2TT, United Kingdom
3 Dept. of Physics & Astronomy, University of Leeds, Woodhouse Lane Leeds LS2 9JT, United Kingdom
4 USRA/LHEA, Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
* Chargé de Recherches FNRS, Belgium
We discuss an ASCA observation of the eccentric WC8 + O7.5III binary
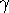 2 Velorum near apastron.
The X-ray spectrum is compared to two previous observations obtained
when the system was near periastron. All three spectra display a hard
emission component that undergoes strong variability over the orbital
cycle. The properties of the hard X-ray emission of
2 Velorum near apastron.
The X-ray spectrum is compared to two previous observations obtained
when the system was near periastron. All three spectra display a hard
emission component that undergoes strong variability over the orbital
cycle. The properties of the hard X-ray emission of
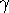 2 Vel are constrained by
taking into account the contribution from contaminating soft X-ray
sources in the vicinity of
2 Vel are constrained by
taking into account the contribution from contaminating soft X-ray
sources in the vicinity of 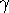 2
Vel. We find that the observed variations are in qualitative
agreement with the predictions of colliding wind models. We investigate
for the first time the effect of uncertainties in the chemical composition
of the X-ray emitting plasma on our understanding of the high energy
properties of the wind interaction region. Our results indicate that
these uncertainties significantly affect the derived shock temperature
and absorption column, but play a smaller role in determining the intrinsic
X-ray luminosity of the colliding wind zone. We further find that the
intrinsic luminosity from the hard X-ray component in
2
Vel. We find that the observed variations are in qualitative
agreement with the predictions of colliding wind models. We investigate
for the first time the effect of uncertainties in the chemical composition
of the X-ray emitting plasma on our understanding of the high energy
properties of the wind interaction region. Our results indicate that
these uncertainties significantly affect the derived shock temperature
and absorption column, but play a smaller role in determining the intrinsic
X-ray luminosity of the colliding wind zone. We further find that the
intrinsic luminosity from the hard X-ray component in
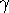 2 Vel does not follow the
1/D distance relation expected from simple models of adiabatic shocks.
2 Vel does not follow the
1/D distance relation expected from simple models of adiabatic shocks.
binaries: general - stars: Wolf-Rayet - stars: individual
(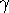 2 Velorum) -
stars: mass-loss - X-rays: stars
2 Velorum) -
stars: mass-loss - X-rays: stars
| Article: |
gamm.ps.gz |
(149739 bytes): |
HTTP |
admin.ago@uliege.be


 2 Velorum
2 Velorum
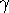 2 Velorum near apastron.
The X-ray spectrum is compared to two previous observations obtained
when the system was near periastron. All three spectra display a hard
emission component that undergoes strong variability over the orbital
cycle. The properties of the hard X-ray emission of
2 Velorum near apastron.
The X-ray spectrum is compared to two previous observations obtained
when the system was near periastron. All three spectra display a hard
emission component that undergoes strong variability over the orbital
cycle. The properties of the hard X-ray emission of
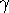 2 Vel are constrained by
taking into account the contribution from contaminating soft X-ray
sources in the vicinity of
2 Vel are constrained by
taking into account the contribution from contaminating soft X-ray
sources in the vicinity of 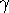 2
Vel. We find that the observed variations are in qualitative
agreement with the predictions of colliding wind models. We investigate
for the first time the effect of uncertainties in the chemical composition
of the X-ray emitting plasma on our understanding of the high energy
properties of the wind interaction region. Our results indicate that
these uncertainties significantly affect the derived shock temperature
and absorption column, but play a smaller role in determining the intrinsic
X-ray luminosity of the colliding wind zone. We further find that the
intrinsic luminosity from the hard X-ray component in
2
Vel. We find that the observed variations are in qualitative
agreement with the predictions of colliding wind models. We investigate
for the first time the effect of uncertainties in the chemical composition
of the X-ray emitting plasma on our understanding of the high energy
properties of the wind interaction region. Our results indicate that
these uncertainties significantly affect the derived shock temperature
and absorption column, but play a smaller role in determining the intrinsic
X-ray luminosity of the colliding wind zone. We further find that the
intrinsic luminosity from the hard X-ray component in
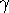 2 Vel does not follow the
1/D distance relation expected from simple models of adiabatic shocks.
2 Vel does not follow the
1/D distance relation expected from simple models of adiabatic shocks.
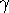 2 Velorum) -
stars: mass-loss - X-rays: stars
2 Velorum) -
stars: mass-loss - X-rays: stars